For digitally beamformed phased arrays, a common implementation method considered for the LO generation is to distribute a common reference frequency to a series of phase-locked loops distributed within the antenna array. With these distributed phase-locked loops, a method for assessing the combined phase noise performance is not well documented in current literature.
In a distributed system, common noise sources are correlated and distributed noise sources, if kept uncorrelated, are reduced when RF signals are combined. This is intuitive to assess for most components in the system. For a phase-locked loop there are noise transfer functions associated with every component in the loop, and their contribution is a function of the control loop and also any frequency translation. This adds complexity when attempting to assess a combined phase noise output. By building upon known phase-locked loop modeling methods, and an assessment of correlated vs. uncorrelated contributors, an approach to track distributed PLL contributions across frequency offsets is presented.


Related Content

RadioThorium in TDD and FDD Configurations
This use case outlines the procedure and profile setting of the RadioThorium module for baseband TDD and IF-mode FDD configurations.

Next-Generation Military Communications Challenges
The next generation of MILCOM platforms will need to leverage more modern communication technologies that have been developed to enable commercial platforms such as cell phones and Wi-Fi.
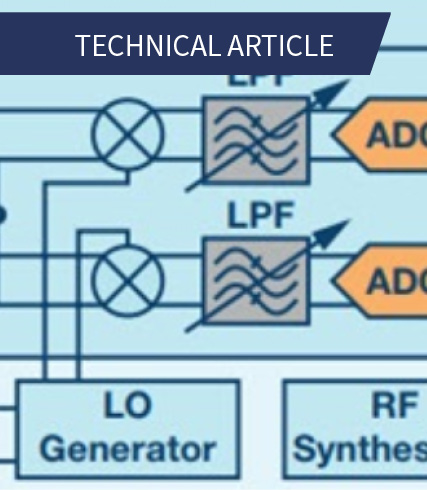
A Review of Wideband RF Receiver Architecture Options
This article compares the benefits and challenges of three common receiver architectures: a heterodyne receiver, a direct sampling receiver.